Overview of 2016 application season
What follows is an edited text of a Webinar that I participated in on the social media site WeChat, Most of the data and advice applies to all students, but my talk was targeted to students applying to US schools from China since WeChat is used by millions of Chinese students.
In 2016, the acceptance rates at the most selective schools fell yet
again. For example, Stanford accepted only 4.7% of its applicants. If we
consider Regular Decision applicants only, the acceptance rates are even lower.
Why is that?
The simple answer
as to why it is harder than ever to get accepted to the top ranked schools In
the US is: statistics.
Let me give just
one example. For the class of 2013, Harvard received 29,144 applications. For
the class entering this fall, Harvard received 39,044 applications. This
represents a 25% increase. At the same time, Harvard did not increase the size
of its incoming class. This helps
explain to a large degree why the acceptance rate has dropped each year.
There are, however,
some other factors that have affected the acceptance rates at top ranked
universities. Students who are applying
to the most selective schools are now applying to many more schools than in the
past. A New York Times article put it
this way: For members of the class of 2015 who are looking at more
competitive colleges, their overtaxed counselors say, 10 applications is now
commonplace; 20 is taking on a familiar ring.
Students are applying to many more schools
because it is much more difficult to predict where even a very strong student
will get in because the competition is so fierce. One student might get into Stanford
but be turned down at Brown and Yale. Another might get into Dartmouth but end
up wait listed at Princeton and Columbia. The increase in applications from top
students only makes getting in that much more difficult for any individual. The
Common Application, the platform that hundreds of the schools in the US use,
permits students to submit information to multiple schools with the press of a
button (and an application fee).
In
addition, universities are getting more effective at marketing. Schools are
increasing their outreach to certain populations, especially under-represented
students or low-income students in the US. Many of the top schools give full
financial aid to US citizens that are offered admission. (Only 5 schools in the
US are need blind for international students). More low-income students are
applying because the schools have reached out to them by buying their names and
addresses in order to send them materials.
On the other hand,
the number of international students applying to the top 30 universities in the
US increases each year too-- students from around the world are seeking to
further their education in the US. This has been particularly true for students
in China. The number of applications filed by Chinese students has increased dramatically
and so have the number of Chinese students enrolling in US universities and
colleges. In 2004-5 there were 63,000 Chinese students studying in the US. Now
there are over 300,000. What this growth means is that applications have soared
from Chinese students, and not just at the most selective schools, but at
virtually every kind of school in the US.
What some students and
families from China do not realize is that admission offices at selective
colleges attempt to bring a diverse class of students from around the US and
the world. In order to do this they have to limit the number of students they
will offer admission to from any given country. Since China sends the most
applications to US schools, it is true that it is harder to get in from China
than any other country. The low acceptance rates quoted by schools are for the
whole student body. If the acceptance rates for students from China were
published, they would actually be even lower than the already daunting overall
percentages.
An article published in The
Economist puts it this way: "Competition
for entrance into these schools is ferocious. Of the roughly 40,000 Chinese
students applying to universities in the United States last year, around 200
were accepted into Ivy League schools. As a Beijing-based consultant puts it
drily: “Harvard only accepts seven or eight Chinese students a year, and one of
them is bound to be the offspring of a tycoon or a leader.” American applicants
have it easy by comparison. The Massachusetts Institute of Technology, for
example, accepted 9.7% of domestic applicants in 2015 – and a mere 3% of
international applicants."
One other factor that significantly affects
the rates of offers of admission is whether a student chooses to apply Early
Decision instead of regular decision. Early Decision is a binding program: students
who are accepted early must withdraw their applications from all other
universities and enroll in the ED school. Universities implement these programs
as it permits them to enroll strong students without worry about losing them to
other schools. In most cases, the difference in acceptance rates between ED and
regular for the top universities is at least 10%. Some schools, like U Penn,
tell students that they improve their chances if they apply early. Duke, this
year, took half of its class early decision. For those students who clearly
have a first choice then early decision is a good option.
There is also a program called Early Action.
Students apply in November and hear prior to regular decision deadlines
(typically January 1). Students offered a spot in Early Action also receive a
boost in admission. The difference in
acceptance rates between early action and regular decision is not as dramatic
as that between early decision and regular decision. I encourage students from
China to apply to at least one school early action. If a student gets accepted
early action he or she can decide before the regular decision deadline of
January 1 whether or not to apply to more schools or to pay a deposit and enroll
at the early action school. Students accepted early action may still apply to
other schools and have until the national candidates replay date of May 1 to
put down a deposit
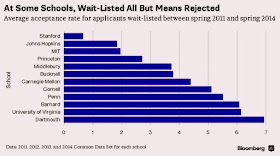
Why are so many students put on the waitlist?
First of all, it might be useful to
give some idea of how steep the odds are of getting off the wait list are for
students who have applied to highly selective universities. To give just one example, last year the total size of the incoming class at Carnegie Mellon
University was 1,557. CMU placed 5,526 on the waiting list . They offered
admission to only 4 of them.
For the purposes of creating a thought
experiment, let’s say the May 1 deadline has just passed and one particular
university is now looking over their numbers and sees it has 40 spaces to fill.
They have over 2000 students on the waiting list. Why would this school have
such a large waiting list and why would they not have them ranked? And if they do not rank students how will
they go about doing this?
At first this seems like a huge task and that having a ranked waiting list would make it far easier to select students. While this initially might seem like a good idea there are many reasons almost no school follows this approach.
Each school has its own mission and institutional priorities that they hope to fulfill. For example, universities, by their very nature, have separate undergraduate schools within the whole university. In order to make sure they will have the proper numbers of students for each of these schools they will need to put various kinds of students on the waiting list.
At first this seems like a huge task and that having a ranked waiting list would make it far easier to select students. While this initially might seem like a good idea there are many reasons almost no school follows this approach.
Each school has its own mission and institutional priorities that they hope to fulfill. For example, universities, by their very nature, have separate undergraduate schools within the whole university. In order to make sure they will have the proper numbers of students for each of these schools they will need to put various kinds of students on the waiting list.
In this thought experiment let’s say
the university has a school of arts and sciences, a school of business, and a
school of engineering. It may well be that the students who have made a deposit
have filled the spaces for engineering and only have a couple for business, but
they have 50 spaces in arts and sciences to fill. Virtually every one accepted
off the wait list will be in the arts and sciences pool. No one will get in to
engineering and perhaps two or three to business.
Institutional priorities also come into play in many other ways too. If, for example, the school in question is State Affiliated, then it may be that the number of in state students is low and the number of out of state students is just about right. In this scenario, all the offers from the wait list would go to in state students. The school will place a large number of both in state, out of state and international students on the wait list to make sure they have enough of each group in case one or more of them comes up short on May 1.
Or let’s say a private school, hoping to increase their geographical diversity, notices that there are very few students who have accepted offers live in States west of the Mississippi. They may decide to pull all those students on the waiting list who are residents of those states and offer almost all the spaces to them. Some schools wish to demonstrate on their profile that they enroll students from many places. They want the perspective these students may bring but they also want more applications to come in too. In some cases schools want to increase their global footprint and therefore focus on taking more international students from the wait list.
Institutional priorities also come into play in many other ways too. If, for example, the school in question is State Affiliated, then it may be that the number of in state students is low and the number of out of state students is just about right. In this scenario, all the offers from the wait list would go to in state students. The school will place a large number of both in state, out of state and international students on the wait list to make sure they have enough of each group in case one or more of them comes up short on May 1.
Or let’s say a private school, hoping to increase their geographical diversity, notices that there are very few students who have accepted offers live in States west of the Mississippi. They may decide to pull all those students on the waiting list who are residents of those states and offer almost all the spaces to them. Some schools wish to demonstrate on their profile that they enroll students from many places. They want the perspective these students may bring but they also want more applications to come in too. In some cases schools want to increase their global footprint and therefore focus on taking more international students from the wait list.
Or it may be that a given school the
percentage of women the school would like to enroll is several percentage
points higher that would they would like. They may then decide to give almost
all the wait list spaces to males.
Or it may be that the number of under-represented students is not what they had hoped it would be, so they may try to enroll as many of these students as they can from off the waiting list. For those who think this sounds like schools have quotas, they don’t. There is no fixed number of students that schools establish as that would violate the law, but there are intuitional goals.
Given what I have just described about schools, I hope it is now clear why schools put many students on the wait list but rarely rank students. The wait list is one way a school gets to shape the class in terms of institutional priorities. If the school tried to rank students it would not be useful as the school does not yet know what groups of students they may be looking for. In other words, the wait list is not so much about individual students, although this is true to some degree; it is more about which groups the school wants to fill in based on what they already know about the incoming class.
Or it may be that the number of under-represented students is not what they had hoped it would be, so they may try to enroll as many of these students as they can from off the waiting list. For those who think this sounds like schools have quotas, they don’t. There is no fixed number of students that schools establish as that would violate the law, but there are intuitional goals.
Given what I have just described about schools, I hope it is now clear why schools put many students on the wait list but rarely rank students. The wait list is one way a school gets to shape the class in terms of institutional priorities. If the school tried to rank students it would not be useful as the school does not yet know what groups of students they may be looking for. In other words, the wait list is not so much about individual students, although this is true to some degree; it is more about which groups the school wants to fill in based on what they already know about the incoming class.
Finally, it is worth repeating that it
is rare for more than a few dozen students to get selected from the wait list
at highly selective schools. Students who are on a waiting list should
concentrate on getting excited about the school they have been accepted to.
Compared to 2015, was the 2016 season easier or more difficult?
For most individuals and groups, 2016
was a year in which it was more difficult to receive an offer of admission from
a highly selective college or university. The number of applications increased
for almost all these schools and very few increased the size of their incoming
classes. The acceptance rates for top ranked schools have steadily declined for
well over a generation. It is not only the Ivies and other top ranked schools
that have seen dramatic increases in applications; the schools that are close
to the top 50-75 colleges and universities have also seen dramatic increases in
applications. Schools that were, even a
few years ago, selective for students from China have now become exceptionally
competitive. (e.g. Georgia Tech).
The good news, however, is that most of
the other 4000 other colleges and universities are looking to enroll good
students from China. Students who have adequate academic performance on the
TOEFL and SAT and present a solid a transcript have a good chance of getting in
to the vast majority of these schools. But there is one addition to academic
credentials that is becoming increasing important to admission decisions—the
ability to pay. More and more
universities in the US need to enroll students who can pay full fees. This is
one of the reasons for the vast increase in the numbers of students from China
who have been offered admission, Some schools admit hundreds and a few offer
admission to well over 1000. Both Michigan State and Purdue enrolled more than
1000 new students from China last year. If Chinese students look at the larger
picture they can find wonderful schools to go to in the US.
What factors affected college applications in 2016 season?
Overall, the
demographic trends in the US show that the number of people in the 18-25-age
range has declined. What this means is that almost half the private colleges
and universities in the US have seen a decline in enrollments. These schools
did not meet their enrolment goals. Many schools, therefore, are doing more
than ever to increase the number of international students on campus as a way
of filling the class and filling them with full payers.
In addition, the
most selective schools are now looking to increase the diversity of the
students that they accept from China. Diversity is a vague word, however, and
it means many different things in admission. One that affects Chinese students
is geographical diversity. While most of the students admitted to top schools
still tend to come from a few cities-- Beijing, Shanghai, Nanjing, Shenzhen--
there has been greater outreach to other cities around China.
More importantly, a
few schools have begun to target low-income students from China. A recent Guardian news story
describes this outreach:
“Ivy League schools have started recruiting
more economically diverse students from China after receiving multi-million
dollar grants from public and private donors. Chinese billionaire real
estate couple, Pan Shiyi and Zhang Xin, gifted $100 million to top U.S.
universities last year- including $10 million to Yale and $15 million to
Harvard – in a bid to help poor students from their home country.” The article
goes on to state, “The admissions directors at Yale and Harvard say the
investment they have received will help create the diversity sought by students
and faculty. ‘We want to make sure that we get the most talented students from
every corner of the world, and it’s just that simple,’ Harvard Dean of
Admissions William Fitzsimmons said.”
Only a handful
of schools are need-blind for international students but the influx of money
from donors for Chinese students will help some highly qualified lower income
students to attend top schools. In order to satisfy the donors, these schools
will make an effort to enroll at least a few low-income students from China
each year.
What factors affected graduate school applications in the 2016 season
The most important
trend for graduate students from China is the decline in applications and
enrolled students. According to the most recent statistics: “Between Fall 2014
and Fall 2015, and continuing a three‐year
trend, applications declined among prospective graduate students from China (‐2%).”
The reasons behind
this drop have in part to do with a change on the part of the Chinese
government. Recently, there has been an effort to keep more students at home
instead of going abroad. As a result, I expect that applications from graduate
students will continue to drop. The Chinese government has done far more than
simply encourage students to stay. They have invested heavily into making domestic
and universities rise in the international rankings. They have done this by
building facilities that will promote innovation and a wide range of subjects,
but particularly in STEM fields. The Wall Street Journal describes the influx
of economic support this way:
Longer term, China is working to upgrade its
own education system to keep more of its students at home and attract others
from abroad. Beijing has poured billions of dollars into its universities in
recent years.
In the US, many
research universities have experienced significant budget cuts over the past
decade and many have had to cut back on research and graduate programs. This is
particularly true of State supported universities. In addition, some of the
labs in China now rival those at many of the well-known research universities
in the US. Chinese student can now stay at home and receive an education tat
can rival or exceed those of many universities in the US.
What has not yet
received much attention but which may actually be masking the true drop in
Chinese graduate student applications has to do with what is happening to the
large number of Chinese students who have received an undergraduate degree in
the past several years. As the number of
Chinese students who come to the US for undergraduate programs has skyrocketed
the number of students who, after graduation, stay in the US for practical
training in hopes of getting real job experience for one year has increased
too. Unfortunately, the US government has not increased significantly the
number of HIB work visas for international people from around the world. Some
Chinese students have jobs lined up in the US but they are not awarded an H-1 visa.
The government uses a lottery system to
determine who chosen to receives the H-1. It used to be that over 75% of those
applying for work visas were approved. Now, due to the vast increase in
international students the percentage approved is less than 30%. What a large
number of these students who do not receive a visa do is to apply to graduate
programs in order to stay in the US. They do this in order to increase their
chances of finding a good job in the US (or, increasingly frequently back in
China). To fill the need for these students many top ranked schools over the last
ten years have created Masters programs in a wide variety of fields (finance,
international business, engineering science etc.). These programs are expensive
and are to some degree moneymaking ventures for the schools. These are not PhD
programs that are used in most rankings of graduate schools. In some cases
students receive a Masters degree from a school with prestigious name, but the
skills learned are not nearly as deep as a PhD or MBA program. I encourage students to do a lot of research into Masters programs before making
the commitment to attend. Some of them are composed mostly of international
students and do not always help student find good jobs afterward. If these
students were not counted in the graduate school attendance numbers the overall
drop in Chinese applications would be even higher than is currently reported.
What makes Chinese students stand out, beyond excellent test scores (for
2016 season)?
For students who are hoping to get into
a highly selective university they will need to do more than just present strong
grades and test scores. These are a necessary but not sufficient part of what
students must have. Coming to the US (and other countries too) has become what
most families who are well off in China want their children to do. Here is how The Economist describes this
trend:
Among Western educators, the
Chinese system is famous for producing an elite corps of high-school students
who regularly finish at the top of global test rankings, far ahead of their
American and British counterparts. Yet so many Chinese families are now opting
out of this system that selling education to Chinese students has become a
profitable business for the West. They now account for nearly a third of all
foreign students in America, contributing $9.8 billion a year to the United
States’ economy. In Britain, too, Chinese students top the international lists.
And the outflow shows no sign of subsiding: according to a recent Hurun Report, an annual survey of
China’s elite, 80% of the country’s wealthy families plan to send their
children abroad for education.
The large number of academically
qualified students who apply to top schools from China makes it difficult for
individuals to stand out. What I tell students they need to do is to become a
subset of 1. By this I mean that the student has to come across as a unique
individual. The ones who do this most readily are often exceptionally gifted in
some way (international/national recognition in academics or other endeavors).
If a student is the gold medal winner in the chemistry Olympiad then their chances
of getting into top schools is quite good. Or if, to site another example, a student has won an intentional competition
in public speaking then her chances will be good she will get accepted to a top
school. But there are lots of ways that students can stand out other than
being a star at something on an international stage. One way is to have a unique voice; another is to
have a demonstrated passion.
Almost anyone who talks about great
writing believes that the key is to have a voice. By voice I don’t mean you
have to write more beautifully than almost anyone in the world. After all, English
is the second language for students from China. In fact, essays from Chinese
students that sound as if they were written by published authors are often
looked at with suspicion. Instead, your words should convey a sense of who you
are that can’t be mistaken for someone else. This year, for example, a student
I worked with wrote a wonderful essay about Star Wars. (I have posted it on my
blog.) Another wrote a great essay about cupcakes and baking. Both of these students
were accepted to highly selective universities. In a successful essay isn’t often
the topic that matters as much as the way the writer conveys something that
stands out. To do this, of course,
requires a lot of work. Choosing a topic, writing drafts and spending time with
words are what help your voice to sing.
Another way students can present their
voice is through interviews. Some schools offer interviews with admission
personnel; others, with alumni. If available, students from China (or anywhere
else) should sign up for an interview. It will permit you to demonstrate your
ability to communicate in English and to talk about yourself in ways that can
help you stand out. In addition to
school related interviews, there are at least two companies that interview Chinese
students and make the interviews available to colleges. Both Initialview and
Vericant interview students in ways that demonstrate speaking ability and
fluency in answering questions about activities and interests. I know the
founders of both and they are wonderful people committed to helping students
and universities create good matches. The fees they charge for these services
are inexpensive and well worth the investment. Most highly selective schools
will not admit students who have not been interviewed. Therefore, interview
prep is something all students applying to these schools should do. At the same
time, no one should go into an interview for a school, internship or job
without some practice and advice from people who know how to prepare students.
Many students from China join clubs
because they think they will look good on applications. It is true that
universities look for students who do more than just do well academically. They
want to enroll students who will contribute both in and out of the classroom. Those
students who get involved with things they really care about and keep with them
over several years will stand out over those who have many different activities
but little commitment to them. Schools increasingly focus on the few activities
that you have spent lots of time with rather than looking for long lists of
activities.
Finding a passion or two can be a
challenge at an early age and not everyone can do it, but trying new things early
on in secondary school will likely lead to a few activities that matter to the student. If
students develop leadership or become sincerely involved, then service admission
officers will note this as an important part of their evaluation. Thee are several studies that show that students who are involved in activities for more than one year do better academically in school and life:
"The predictive power of follow-through was striking: After controlling for high school grades and SAT scores, follow-through in high school extracurriculars predicted graduating from college with academic honors better than any variable." Angela Duckworth, Grit: The Power of Passion and Perseverance.
For those
students who attend the international sections of their schools in China it is
easier to get involved in activities as the administration is aware of the
importance of supplementing applications with more than academics in order to get accepted to highly ranked colleges. Those
students enrolled in programs dedicated to taking the gaokao might have a hard
time finding something in the school to be a part of, but there are many things outside of school
that might help them develop skills and character
traits that will not only help to get into college but will help in life too.
How are Chinese applicants disadvantaged in the application process?
Unfortunately,
Chinese students face some difficulties getting into top schools because of
issues centered on academic integrity. There are many agents in China who work
with students. Some of the agents are wonderful and help in ethical ways. On the
other hand, there are many who alter transcripts, manufacture recommendations,
and write essays and resumes for the students. There have been many news stories in the US media about cheating on the SAT in Asia. As a result, applications
from China are looked at with suspicion:
"The reality is for international students, particularly in Asia, there’s a worry about whether the application is authentic, whether the essay is authentic, whether the person who shows up at your door is the same person who applied,” said Joyce E. Smith, chief executive of the National Association for College Admission Counseling in Arlington, Virginia"
This trend to see students from China as cheaters is, to say the least, unfortunate, as those students
who do things ethically must somehow overcome negative stereotypes. The actions
of unethical agents have hurt the reputation of students in the US. Schools should do more to check the credentials of Chinese students. Students
should only work with ethical agents, counselors and companies.
What do admission officers think about applications from China? What do
they usually expect?
Admission officers
at highly selective universities and colleges approach applicants from China
with very high expectations. They have seen the quality and number of applicants
increase each year. Students must have superior standardized test scores to get
a close look. An article in the China Daily that quotes a private counselor in
China puts it this way:
We've found that students should score
higher than 110 (out of 120) on the TOEFL and 2,200 (out of 2,400) in the SAT
to secure their admission to prestigious American universities. But in previous
years, more than 105 in TOEFL and more than 2,100 on the SAT was
adequate," he said.
These
high numbers are only one part of the high expectations admissions officers
have about Chinese students. Most students now have done some sort of service
work, either in school, or the community or over the summer in a different
location in China or country. Schools like to see students who care for their
country and community.
Colleges
and universities also want to see some significant commitment to a few
activities. There are, however, no “right” activities. Students can have a passion for almost
anything that will help them to stand out. Another characteristic that schools
often look for is leadership. Schools, especially highly selective schools,
hope their students will become leaders in the world after they graduate.
Therefore, they look for students who have already developed some of the traits
that predict future leadership and success.
In
addition, schools often hope to see that a student has done something
significant over the summer. Many students think this means going to the US for
programs offered by universities. Unless these programs are highly selective, summer
programs in the US do not have much of a positive effect on admission. Instead,
students should try to find projects that will supplement their own interests.
A student might do an internship, or get involved with service, or supplement
their education by learning a skill such as coding.
At
the same time, schools also want to see that students know well the college or
university they are applying to. Most schools now ask the question ”Why are you
interested in our school?” Students who
do not have detailed and concrete answers are at a disadvantage. Applying to a
school because it has a high ranking is not a good reason to want to attend; instead,
students should have specific reasons: for example, a student who has reached out
to faculty to find out about courses or research opportunities demonstrate
interest in the programs and school in ways that stand out. It is also
important to note that more schools are using demonstrated interest as an
important part of the admission evaluation. If a student can visit the school
itself, can sign up for an interview and respond to any outreach on the part of
the school this may help them get in.
What do you think about 2017 Fall application season?
For the 2017
application season I would predict that applications will again increase for
the most selective schools. This means that acceptance rates will again drop
making it vital that students come up with a list of schools to apply to that
include some schools where they are likely to get admitted.
Many students will
be taking a variety of standardized tests for admission. More international
students are now signing up to take the ACT instead of or in addition to the
SAT. The majority of US students now take the ACT.
On the other hand,
this year will mark the first time that students will take and submit scores
from the newly designed SAT. The first testing shows that average scores are
about 90 points higher than the previous version. While this should not affect
admission significantly, any test takers will now think the test is easier than
it was before.
In addition to new
testing, there is also a new platform that students can use to apply to 93 universities. The Coalition for Access
and Affordability has launched an alternative application to the Common Application.
The essay questions are slightly different and the format is different. The
schools that will use this form consist of many of the most selective schools
in the US. One thing this platform permits is for students to submit extra materials
to be stored in what they call a “virtual locker”. Students can store
presentations, videos, etc. and permit schools to look at them. Many in
education are worried that students will submit too much material. Agents may
advertise the virtual locker in ways that will encourage students to use their
services. I am worried that students will submit materials that will not help
with admission and may in fact hurt if admission readers feel that the students
have had too much help with this new platform.
Finally, a report came out this year from Harvard’s education school called Turning the Tide. It has the
support of many of the top universities in the US. The report makes a significant
number of recommendations about how students should approach their education
and experience in high school. They also recommend how colleges should change
the way they evaluate students for admission. It is difficult to say how many
schools will implement any of these recommendations and in what way this will
affect which students from China (or any place else) will be evaluated in ways
that are significantly different than in previous years. The emphasis on service
and community, however, does send a message that schools will be looking for
students who have far more to bring to a campus than just strong test scores.
Students may wish to contact universities they are interested in to ask how
they may incorporate the report’s recommendations.






Excellent post,YouTube is one of the standard sources to get the money. It is incredibly difficult to the new part to win the titanic money but you can check http://www.mphpersonalstatement.com/writers/ to manage your essay work. The reason is that new part should post some hypnotizing archives which are related to the fundamental subject.
ReplyDelete